Diabetic Neuropathy
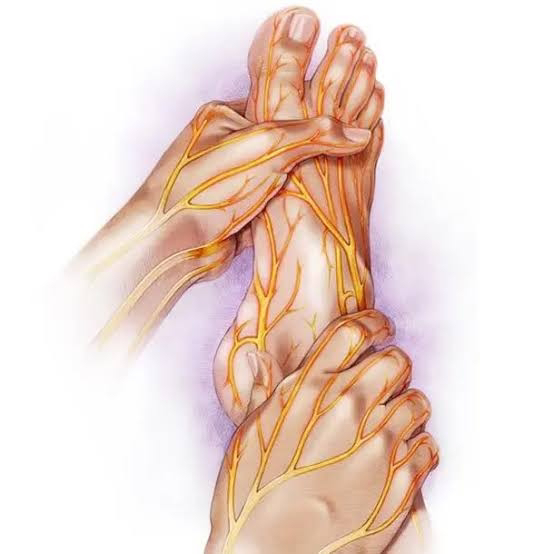
What is Diabetic Neuropathy?
Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that can happen if you have diabetes. High blood sugar levels can harm nerves throughout your body, but diabetic neuropathy most often damages nerves in your legs and feet.
Types of Diabetic Neuropathy
1. Peripheral Neuropathy: This is the most common type and affects the feet and legs first, followed by the hands and arms. Symptoms include numbness, tingling, pain, or weakness in these areas.
2. Autonomic Neuropathy: This affects the nerves that control your internal organs, leading to issues with your heart, digestive system, bladder, and sex organs.
3. Proximal Neuropathy: This type affects the hips, thighs, or buttocks and can cause severe pain and muscle weakness.
4. Focal Neuropathy: This affects specific nerves, often in the head, torso, or leg. It may cause sudden weakness or pain.
Symptoms of Diabetic Neuropathy
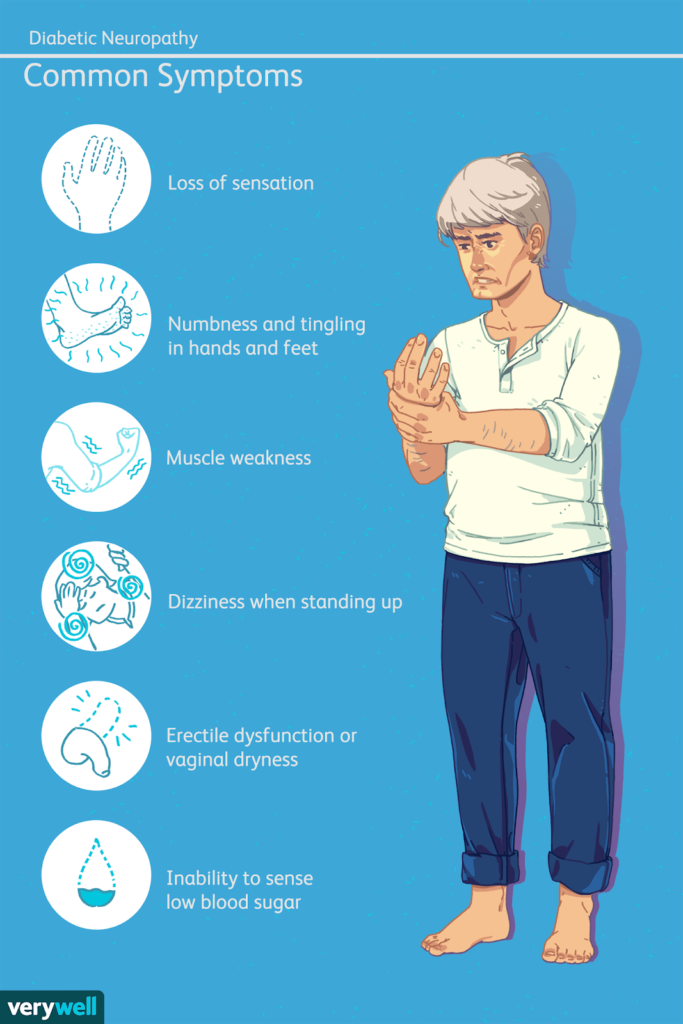
– 1.Numbness or reduced ability to feel pain or temperature changes**
– 2.Tingling or burning sensations**
– 3. Sharp pains or cramps**
4- increased sensitivity to touch**
-5. Muscle weakness**
– 6. Loss of reflexes, especially in the ankle**
– 7. Loss of balance and coordination**
For autonomic neuropathy, symptoms may include problems with digestion, bladder control, heart rate, and sexual function.
Causes
The main cause of diabetic neuropathy is prolonged exposure to high blood sugar levels, which can damage nerves and the small blood vessels that nourish them.
Risk Factors
– Poor blood sugar control: Keeping your blood sugar consistently high increases the risk of every diabetes complication, including nerve damage.
– Duration of diabetes: The longer you have diabetes, especially if your blood sugar isn’t well-controlled, the greater the risk of neuropathy.
: Diabetes can damage the kidneys, which can increase the toxins in the blood and contribute to nerve damage.
– Smoking: Smoking narrows and hardens your arteries, reducing blood flow to your legs and feet.
Prevention
– Keep your blood sugar levels under control: Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly and take steps to keep them within your target range.
– Follow a healthy diet and exercise routine: Eating a balanced diet and staying active can help you manage your blood sugar levels.
– Take care of your feet: Check your feet daily for blisters, cuts, or sores. Wear comfortable shoes and keep your feet clean and dry.
– Avoid smoking: If you smoke, seek help to quit.
Treatment
While there is no cure for diabetic neuropathy, treatments can help manage the symptoms:
– Medications: Pain relievers, antidepressants, and anti-seizure drugs can help manage pain.
– Therapies: Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and specific exercises can help with muscle weakness and pain.
– Foot care: Regular check-ups with a podiatrist and proper foot care can prevent complications.
– Blood sugar management: Keeping your blood sugar levels within your target range can prevent the progression of neuropathy.
Conclusion
Diabetic neuropathy is a common complication of diabetes, but with proper management and care, its impact can be minimized. Maintaining good blood sugar control, taking care of your feet, and leading a healthy lifestyle are key steps in managing diabetic neuropathy and improving your quality of life. If you experience symptoms of neuropathy, consult your healthcare provider for appropriate treatment and support.